ABT Framework Student Resource Page Round 33 – Counterpart International
Contents
Working Circles
Course Dates & Time
Sign up to host your Working Circle here (separate page)
Sign up to participate in Working Circles (separate page)
Before the first class
Session 1 Resources – Intro, Outer Circle, Content Vs Form
Session 2 Resources – Singular Narrative
Session 3 Resources – Hero’s Journey
Session 4 Resources – Nested ABTs and WHAT/HOW
Session 5 Resources – Proposals with Dianna Padilla
Session 6 Resources – Audience as Hero with Park Howell
Session 7 Resources – Listening with Brian Palermo
Session 8 Resources – Narrative Spiral with Nancy Knowlton
Session 9 Resources – Abstract Analysis
Session 10 Resources – Narrative is Leadership
ABT Framework Google Group
Social Media
Working Circles
Synopsis on Working Circles – If you’re new to Working Circles, start by reading this.
Working Circle Half Hour Schedule – Use this to guide you through how to host your half hour Working Circle. To complete the class, you must sign up to host 1 Working Circle and sign up to participate in 2 Working Circles.
Sign up to host a Working Circle
- Pick an available half hour time slot on this page.
- Fill in your first name, last name, and a short title for your Working Circle based on your ABT.
Host responsibilities
- Email your participants your ABT before the Working Circle so they have time to review it – we’ll send you the list of your participants’ email addresses 3-5 days ahead of time.
- You can send your participants a revised ABT of what you originally submitted to class or use a brand new ABT all together.
- During the Working Circle, use the ABT Blue Card and follow the half hour schedule.
- You’re the moderator of the discussion, so do your best to make sure everyone gets a chance to speak and provide input.
- We’ll send you and your participants a Zoom link for your Working Circle 3-5 days before you’re scheduled to host, so no need to worry about that.
Participant responsibilities
- Sign up to participate in a minimum of 2 Working Circles. Sign up here.
- Review the ABT that the host sent you ahead of time and come up with your version of the 5 Word Problem (this will be discussed in class) for the host’s ABT before the Working Circle starts.
- One participant should volunteer to be the notetaking Scribe. The Scribe will share their screen so that everyone can view it and have a Word document up to take notes. You can find a premade Scribe document in Word here.
- (Optional) Participants can rewrite the host’s ABT and present the rewritten ABT to the host during the Working Circle. This approach is for participants who want a little extra practice and to give the host more options and ideas for rewriting their ABT. So far we’ve had reports back that hosts are incredibly grateful when participants do this.
- Be prepared to use the ABT Blue Card and all the tools you’ve learned in class to help the host clarify their narrative.
Course Dates and Times
Tuesday/Thursdays First class Tuesday March 7 @ 1:00 PM PST (Los Angeles Time) / 4:00 PM EST
March: 7, 9, 14, 16, 21, 23, 28, 30
April: 4, 6
Before the first class
Sign up to host a Working Circle
Download the ABT Blue Card – Have it open or printed out and ready for each class.
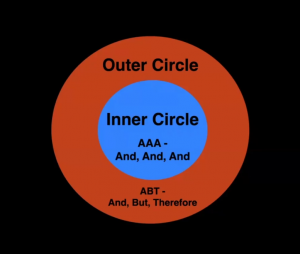
Session 1 Resources – Intro, Outer Circle, Content Vs Form
Inner & Outer Circle
The latest ABT Time Podcast Episode where Randy and Matthew discuss the latest developments in narrative:
If you haven’t signed up yet to host a Working Circle, be sure to do so here.
Uri Hasson’s Paper on Neurocinematics – For a look at how narrative and non-narrative effects the brain.
Optional Exercise #1 – “This is a story of…” – Change
This is an exercise that would be handy to have done before your in class ABT Build with Matthew because Matthew asks this question for roughly 99% of ABT Builds.
For this exercise, tell us what your ABT is about by finishing this sentence and using only 3 additional words “This is a story of____.”
It seems simple, but this exercise is tricky because participants tend to focus on the subject. But stories need more than a subject, they need change. Look at your ABT and see what major change you want to occur. Your story starts at point A and ends at point B – what’s the change that you want to get us to point B?
Examples of changes in past ABTs:
- Protecting a species
- Strategizing building restoration
- Managing conservation efforts
- Restoring wildlife
- Adapting to change
- Educating our stakeholders
Look at this example ABT:
Congressional funding is a key requirement for the continuation of important avian research, and we know that our research allows us to be better able to manage our wildlife habitats and protect endangered species. But program managers don’t feel confident about securing future funding because some research areas are not receiving enough attention. Therefore, we need to effectively promote the proven success in these research areas to secure future funding.
When asked to complete the sentence “This is a story of____,” a possibility is “This is a story of avian research.” But this is just the subject and it doesn’t tell us what change is taking place in this story.
Instead of the subject (avian research), focus on the change. If you wanted the change for the broader story, then you might say “secure,” since ultimately the purpose is to secure the future funds. “This is a story of securing future funding.”
“Securing future funding” is the broader change that you want to have happen, but you can take it down to a narrower level by focusing on the specific change you want to go through to get that future funding: “This is a story of promoting our successes.”
Point A of the story: We are not promoting our successes.
Point B of the Story: We are promoting our successes.
Try to fill in “This is a story of____” for your ABT using only 3 additional words (focusing on the change) or less.
Session 2 Resources – Singular Narrative
The One Thing:
Nicholas Kristof’s Advice for Saving the World – The importance of the singular narrative. Once you increase the size of a narrative from one person in need to two people in need, compassion drops in the audience.
Compassion Fade: Affect and Charity Are Greatest for a Single Child in Need – The research article that “Advice for Saving the World” references.
‘Data-Driven’ Campaigns Are Killing the Democratic Party – The article in which Dave Gold coined the term “Christmas Tree” when looking for an overarching problem. It’s okay to have several problems in your narrative, but you need to find the overarching Christmas Tree problem for your narrative that all the other problems can hang off of like ornaments.
Off With the Talking Heads: A Plea for One COVID Voice – Randy’s recent Medpage article where he talks about the importance of the singular narrative.
Optional Exercise #2: Using the Dobzhansky Template to find your “One Thing.”
Restructure your ABT in the form of a Dobzhansky Template to help you find your singular narrative. This is an excellent tool to use during Step 1 of the ABT Blue Card.
Dobzhansky Template: Nothing in _______ makes sense, except in the light of ________.
Examples: Nothing in biology makes sense, except in the light of evolution.
Nothing in geology makes sense, except in the light of plate tectonics.
Nothing in the management of mule deer makes sense except in the light of correctly estimating abundance.
Nothing in the challenge of teaching human anatomy makes sense except in the light of time management.
Session 3 Resources – Hero’s Journey
Matthew Winkler Video: What makes a hero? – We only watched the first two minutes in class. Watch this to the end to see how the hero’s journey applies to your life:
Bankspeak: The Language of World Bank Reports, 1946–2012 – The Literary Lab report on how the World Bank reports are completely unreadable, due in no small part to the overuse of the word “and” to glue together contradicting statements.
A spat over language erupts at the World Bank – The somewhat dismissive Economist article on the “conjunction dysfunction” about the Literary Lab’s report.
Optional Exercise #3: The 5 Word Problem
“What’s the problem?” is the second most common question Matthew asks during the ABT Builds. For this exercise, look at your ABT and try to finish this sentence “The problem is _____” and use only 5 additional words.
Examples: The problem is bad resource management.
The problem is the old method doesn’t work.
The problem is we have bad data.
Stripping down your problem to just 5 words can help you clarify what your narrative is actually all about and focus in on the real problem that you want to address.
Session 4 Resources – Nested ABTs and WHAT/HOW

Oprah’s Golden Globes Speech – A great example of using Nested ABTs. Color coded in the ABT format.
Three Forms of the ABT – It’s recommended you read this excerpt from Houston, We Have a Narrative and get an understanding of the cABT (Conversational ABT).
Optional Exercise #4: cABT – Starting from simplicity
Randy might ask you the cABT version of your ABT, so for this exercise you’ll prepare your cABT ahead of time.
The cABT should have all specifics stripped off of it. Use nothing but generic words, like “thing” and “stuff.” For example, if your ABT dealt with a new way to clean junk from the ocean that’s an improvement and the old system is outdated, the cABT would be “We had a thing we were using for a while, but it’s not working that great, so now we want to use a better thing.”
See? We can’t tell that you’re working on cleaning the environment. You could just as well be telling me that you’re implementing a new accounting system at your bank for all we know. That makes it a good cABT.
This exercise is important in making sure you have an easily understood base narrative, that you really know what the narrative core of your ABT is all about. And then from the base cABT, you can start adding specifics again when constructing your kABT.
Session 5 Resources – Proposal with Dianna Padilla
Advice on how women should pitch the “BUT” – A reply by Dianna to a former student’s question about the bias against women when they use the same strategies as men.
Are You Confused by Scientific Jargon? So Are Scientists – A New York Times article recommended by Dianna about how jargon clogs up scientific papers to the point that other scientists can’t understand them. Remember: your Inner Circle is always smaller than you think it is.
Chaos in the brickyard – A famous Science Magazine letter on scientists and their obsessions.
Optional Exercise #5 : IF/THEN – The tool of HOPE and FEAR
The IF/THEN tool is incredibly powerful at helping to set the stakes and getting very specific. You can use it in the Blue section and it can be a tool for Hope, showing what Heaven could look like it all goes according to plan. Or you can use it for Fear in the Red section, showing how bad Hell can be if everything falls apart.
But what should your IF/THEN be about? To answer that, go back to the optional exercise “This is a story of…” – Processes – Change ‘‘ and find the changes that are taking place in your narrative.
Let’s look at the example we used.
Congressional funding is a key requirement for the continuation of important aviation research, and we know that our research allows us to be better able to manage our wildlife habitats and protect endangered species. But program managers don’t feel confident about securing future funding because some research areas are not receiving enough attention. Therefore, we need to effectively promote the proven success in these research areas to secure future funding.
For the example ABT, the changes where:
Broader change: A story of securing future funding
Specific change: A story of promoting our success.
Now that you have the changes, try crafting them into IF/THEN statements, both positive and negative, and see if you find any variation that has some power. If it helps, you can put them into the form of questions like the ones below for you to answer:
- If you can secure future funding, then what happens? (Hope)
- If you do a good job at promoting our successes, then what happens? (Hope)
- If you can’t secure future funding, then what happens? (Fear)
- If you fail to promote our successes, then what happens? (Fear)
Try asking questions like this for your own ABT’s changes and see if you can properly set the stakes using the tool of Hope or Fear.
Session 6 Resources – Audience as Hero with Park Howell

Kurt Vonnegut on the Shapes of Stories:
Park Howell’s Business of Storytelling Podcast
Learn From My 10-Year Journey With The ABTs of Storytelling – Park Howell’s 400th episode of his Business of Story podcast in which he highlights his favorite moments with the ABT from previous episodes.
Brand Bewitchery: How to Wield the Story Cycle System to Craft Spellbinding Stories for Your Brand – Park Howell’s book on using the ABT and the Hero’s Journey to help market your brand.
The Narrative Gym for Business: Introducing the ABT Framework for Business Communication and Messaging – The business version of the Narrative Gym, written by Park and Randy.
Optional Exercise #6: Past, Present, & Future
There’s a few different variations of the kABT. We’ll be looking at one of them here, the Past-Present-Future ABT.
The Past-Present-Future format isn’t applicable to all topics, but we can experiment and see if it is with yours. For your project, craft the AND in a way to tell the audience what was going on before in your project or your old method for addressing a problem. For the BUT, tell the audience the current problem with the old method of doing things. For the THEREFORE, let us know the solution that you’ll be attempting to implement in the future.
The cABT for a Past-Present-Future ABT might look like: “We were doing this one method for the longest time AND it worked well enough, BUT a new issue came up, THEREFORE now we have to fix it by doing a new thing.”
You could also attempt an IF/THEN in a Past-Present-Future ABT, for example: “We were doing this one method for the longest time AND it worked well enough, BUT a new issue came up and IF we don’t fix it THEN it’s going to get really bad, THEREFORE now we have to fix it by doing a new thing.”
Try filling in the details with your own project and make your own kABT using the Past-Present-Future ABT format.
Or fill in the details with facts about your life to make a Past-Present-Future ABT for introducing yourself at parties or networking events: “I was doing this one thing, BUT then a big issue came up, THEREFORE now I’m focusing on this other thing.”
And you can break out the Past-Present-Future ABT if you’re ever put on the spot by your employer with a question on where you’re at with a project at work. cABT: “Well boss, we got all this stuff done and it’s working great, but now we’ve got a new problem, so we’ll be doing a bunch of steps to fix it.” Fill in the details to that cABT on the fly and your boss should be up to speed on what you’re up to.
Session 7 Resources – Listening with Brian Palermo
Audience focused communication requires listening:

Brian Palermo’s Resources – Brian offers a number of resource videos on his website, some with interactive exercises built in. Topics include listening, utilizing emotional intelligence, and audience focused communication. He also offers online improv training to help improve listening and communication skills.
Don’t Be Such a Scientist, Second Edition: Talking Substance in an Age of Style – In this second edition of Randy’s book, Randy added a brand new chapter: “Don’t Be Such a Poor Listener.”
Rather Than Arming Our Differences, We Need To Embrace Them—and Simply Be NICE – An article on how shared values and first principles can help us bridge divides between different groups. And for the purposes of our course, where do you bridge that divide? The blue section.
Optional Exercise #7: Expected Vs Observed – Leading us to the ideal world
Time to look at a different version of the kABT, the Expected Vs Observed ABT.
The Expected Vs Observed ABT isn’t applicable to all topics, but we can experiment and see if it is with yours. For your project, paint a perfect world in the AND in which everything goes right, what you would Expect from your “ideal world.” Aim for Heaven!
Unlike the Past-Present-Future ABT, this time you’re starting the AND out in the ideal, perfect future, not the past. A positive IF/THEN in the AND is often helpful here in really driving home what the stakes are if all goes according to plan.
Then for the BUT, tell us the problem that you’re Observing which is interfering with this perfect world you envisioned in the AND. Aim for Hell!
Finally, for the THEREFORE, tell us how you’ll lead us out of the problem of the BUT and back to the ideal world of the AND.
(This is often a great ABT for people who work on climate change projects. Climate change has been such an ongoing problem that it’s a part of our past now, so instead of looking at the climate change ridden past, you’re looking at the ideal future where you’re actively solving the problems of climate change in the AND).
A typical Expected Vs Observed cABT: “We’ve got this great project AND IF everything goes to plan THEN we’ll get all kinds of great benefits BUT right now it’s not working because of a problem THEREFORE we need to fix it by doing some stuff.”
Try filling in the details with your own project and make your own kABT using the Expected Vs Observed ABT format.
Session 8 Resources – Narrative Spiral with Nancy Knowlton
The Narrative Spiral:

Individuals with greater science literacy and education have more polarized beliefs on controversial science topics – The paper Nancy referenced that shows how science literacy and political affiliation effect belief in controversial topics. Despite what scientists would like to believe, more information isn’t always the right answer.
Citizens of the Sea: Wondrous Creatures From the Census of Marine Life – Nancy Knowlton’s book.
Earth Optimism – A movement that Nancy is heavily involved in to help highlight the upward rise of the climate movement’s narrative spiral.
Katharine Hayhoe – The Evangelical Christian and Climate Scientist who emphasizes shared values when teaching about climate change.
Optional Exercise #8: Audience as Hero
Time to look at a different version of the kABT, the Audience as Hero ABT.
The Audience as Hero ABT isn’t applicable to all topics, but we can experiment and see if it is with yours. In this ABT format, the audience is the hero of their own hero’s journey, and you (or your organization, process, project, product, etc.) act as the sage/mentor character that guides the audience through the special world to the solution.
Audience as Hero ABTs work best when you have a specific course of action that you want the audience to take, such as to buy a product, vote for a ballot measure, support a conservation movement, etc.
For the AND, start with the ordinary world of what you and the audience can agree on as important, properly setting the stakes for something the audience cares about. (Remember the class on Listening? This is where listening to and knowing your audience comes into play.)
For the BUT, tell us the problem that is putting the audience’s important thing at risk.
For the THEREFORE, you (or your organization, process, project, product, etc.) are introduced as the sage/mentor that guides the audience toward the solution to their problems. Remember, you are not the hero of this ABT, the audience is. You are just the guide.
A typical Audience as Hero cABT: “You know that this thing is important to you for some reasons AND IF you have this thing THEN stuff turns out great, BUT this thing is having a problem, THEREFORE we have the solution you can use to fix this problem.”
Try filling in the details with your own project and make your own kABT using the Audience as Hero ABT format.
Session 9 Resources – Abstract Analysis
Optional Exercise #9: Shared Values – Reaching your audience in the Blue
By now you hopefully have an ABT that helps your audience understand what’s at stake, what the problem is, and what we need to do to fix it. And that ABT should be able to be understood by a broad audience.
But what if your audience isn’t broad. What if you know exactly who they are and what they value? In that case, your ABT should reflect that. Therefore, there’s a place in an ABT that is flexible and adaptable, that you should consider rewriting every time you talk to a different audience – your AND material.
The Blue section of an ABT is the place to reach out to a specific audience, understand what your shared values are, and incorporate them. The AND consists of an Ordinary World and answering the question of What’s at Stake?, and those two points may differ from audience to audience.
For this exercise, pick two different specific audiences and attempt a new AND for each. It could be a specific group of stakeholders, upper level management, a group of scientists with a specific background, an average customer, or any group that you have to reach out to and make them understand where you’re coming from.
For each of the two groups, frame the Ordinary World in such a way as to make your topic important to their values. Do they value making money? Saving lives? Keeping their way of life? Preserving history? Try framing the Ordinary World to include those values.
Is there a way to rework your “What’s at Stake?” by making your IF/THEN more relevant to what they care about?
Work on your AND for each of the two groups, using your Blue material to work on reaching your shared values.
Session 10 Resources – Narrative is Leadership
The Steve Jobs (ABT Brain) and Bill Gates (AAA Brain) interview. Skip to 7:11 for the section that Randy showed in class.
South Park creators Matt Stone and Trey Parker talk about using the ABT’s Rule of Replacement to write episodes:
The Narrative Index – If you’re a person who likes metrics, here’s Randy’s blog post outlining the Narrative Index and how it can be used to determine the narrative strength of a piece of communication. Try it on your own writing!
The ABT Framework Google Group
We have an ABT Framework Google Group set up for all the current students and alumni of the Course. If you join, you’ll be able to create and submit new Working Circles for brand new ABTs for projects that you’re working on to get ABT feedback from others who have trained in this method. And you can participate in new Working Circles from future classes and alumni submissions to help hone your ABT skills.
Also, as graduates of the class, you’re free to come back and audit the entire course for free as often as you like. We post future classes that you can audit to the Google Groups.
To sign up for the ABT Framework Google Group, you can email Matthew (mattmdavid@gmail.com) a Google account email address (i.e. @gmail.com) to be able to visit the page directly. Or you can send him a non-Google address and still participate by receiving email updates from the Google Group whenever new Working Circles are posted or new classes are available that you can audit for free.
Science Needs Story – Randy Olson’s Blog.
@ABTAgenda – Follow Randy on Twitter.
ABT Time Podcast – All things ABT, start to finish. In this weekly hour long post Randy will discuss observations, applications and implications of this powerful tool that is at the core of his narrative training program and effective communication of all forms.
ABT Framework Course & Story Circles Grads – A private Facebook group just for graduates of the course where you can post about any ABT related topic you find around the ‘net. Once you request access, we’ll let you in.
Story Circles & ABT Training – An open-to-all Facebook Fan page.
The ABT Agenda Newsletter – We send out a newsletter a few times a year with new ABT related events, news, and course updates. If you sign up, we promise not to spam you with tons of junk!